Light can be divided into two categories: visible and invisible. The light that the human eye can see includes natural sunlight and light from artificial sources such as cellphones and computer monitors. Unlike visible light, however, invisible light, such as ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B rays, is not detectable by the human eye. This radiation harms your health and causes burns, among other symptoms. Ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B rays range from about 100 nm to about 400 nm (nm stands for nanometer, a measure used when measuring light). Blue light is the next color in the spectrum, with a wavelength of 380 nm to 500 nm. Blue light from 380 nm to 400 nm is known to cause skin damage. As the wavelength approaches 500 nm, the risk appears to slightly reduce.
What is blue light?
Blue lights are present virtually everywhere. It emanates from daylight sun, fluorescent lights and LEDs in objects like phones and TVs. Although digital devices also emit some blue light, it is a small fraction compared to the one we are exposed to from the sun. The risks, however, are amplified by keeping our phones close to our faces and checking them frequently throughout the day. According to a recent survey, millennials check their phones an average of 157 times daily. That’s more than five times as often as the thirty times a day that the average person over 65 checks their phone. As a result, millennials are at significantly higher risk of daily blue light exposure.
What are the effects of blue light on my eyes?
The cornea and lens allow nearly all visible blue light to reach the retina. Since blue light affects our eyes and overall health, it has been linked to a wide range of adverse short- and long-term outcomes. According to scientific research, increased blue light exposure causes a temporary phenomenon called “veiled glare,” associated with temporary visual discomfort (eye strain, dry eyes, burning and sore eyes, itchy eyes, fatigue and headaches). The leading cause of visual impairment, such as age-related macular degeneration, can be a result from unprotected and prolonged exposure to blue light. It can cause severe damage to the retina and progressive degeneration of the macula. This form of vision loss can cause loss of color vision, the ability to read, write, and drive, and other cognitive functions that may ultimately result in total blindness.
How does blue light damage the eye?
High-energy blue light passes through the front of the eye (the cornea and lens) and damages the retina and macula in the back (the fovea). This contributes to oxidation and degeneration of the macular part of the eye throughout a lifetime.
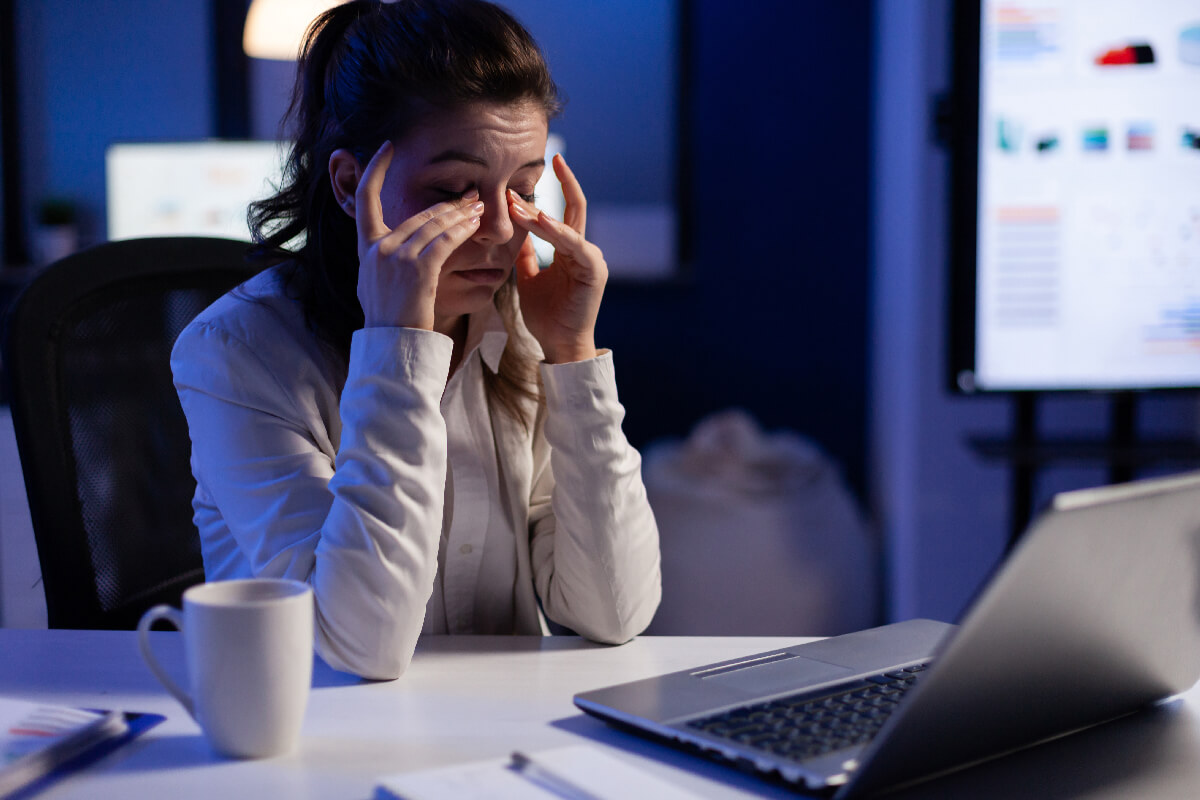
Can blue light cause eye strain?
Blue light emitted by computers and other digital devices can reduce contrast and cause digital eye strain. Eye strain can be caused by several other factors, including lack of sleep, dry eyes, poor lighting, and improper posture while using a computer. Symptoms of eyestrain include the inability to focus and general discomfort in the eyes. Studies suggest that long-term exposure to blue light may damage retinal cells. Eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration, can result.
Can exposure to blue light cause skin damage?
Researchers have discovered that the blue light from our electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, can cause damage to the skin and eyes. Blue light, also known as high-energy visible light (HEV), is linked to skin discoloration, inflammation, and a weakened skin surface due to its role in stimulating photo-aging.
How does blue light affect the skin?
Changes in the skin cells, such as cell shrinkage and death, have been linked to exposure to blue light from electronic devices. Such alterations can occur after as little as 60 minutes of exposure. Skin discoloration may also result from prolonged exposure to blue light. According to a study, people with darker skin were more likely to experience swelling, redness, and pigment changes after exposure to blue light.
Does blue light have any benefit to the skin?
Blue light has damaging and healing effects on the skin, depending on its use. The use of blue light has been shown to reduce the prevalence of precancerous patches and to treat extensive areas of skin with minimal discomfort. In addition to red light, blue light is used in photodynamic treatment, a method of treating cancer in which specific wavelengths of light are used to trigger the action of drugs known as photosensitizing agents. In the case of some cancers, it may be just as effective as surgery and radiation therapy. In addition, photodynamic therapy has little or no adverse effects.
Does blue light affect sleep?
Blue light, more than any other color, disrupts your body’s ability to prepare for sleep by inhibiting the production of melatonin, a hormone that induces sleep. Simply put, you are not as sleepy as usual at night, and it takes you longer to get to sleep under the influence of blue light.
How can I reduce my exposure to blue light?
It is highly recommended that you install a blue light screen protector on your phone. You can use your phone or tablet without worrying about your skin or eyes, as this simple solution is just as effective. This feature that reduces the intensity of the screen’s blue light and replaces it with a warmer yellow glow is referred to as light mode on some smartphones. Keeping your screen at this brightness level is always better for the eyes and may slow the aging process. The other option is to wear glasses that have blue light blocker lenses.
Is it possible to repair the damage done to the eyes by blue light?
Retinal cells can be damaged by blue light. However, the dose and exposure time of blue light required to harm these photoreceptors is still unknown. Unfortunately, the damage is irreversible.
How do I prevent further damage of blue light to my eye?
To protect your eyes from further damage:
- Take breaks from screens regularly.
- Focus on something at least 20 feet away from your screen every 20 minutes.
- Spend at least 20 seconds in this position and stay away from the blue light at night.
Is blue light the most dangerous in the light spectrum?
Of all the colors of light we see, blue light causes the most damage to our eyes. This 400-500 nm energy wavelength range is interpreted as high-energy visible (HEV) light by our eyes.
Can blue lights lead to skin hyperpigmentation?
Recent studies have shown that prolonged exposure to blue light, such as that emitted by your various electronic devices, can cause the skin to react in ways that can accelerate the aging process and cause hyperpigmentation.
Does blue light have the potential to cause melanoma?
New research suggests that blue light exposure may contribute to the malignant transformation of melanocytes, a step that can lead to melanoma.
What effect does sunscreen have on blue light?
Tinted mineral sunscreens use physical ingredients that remain on the skin’s surface after application. Mineral sunscreens are made to deflect UV and blue light away from the skin.

How can I protect myself from skin aging caused by blue light?
- By taking antioxidants
There is no such thing as too much care for your skin, and everyone should incorporate topical antioxidants into their routine. When exposed to light, antioxidants reduce the oxidative stress that results from exposure. Applying an antioxidant serum topically may assist with skin issues like dryness, fine wrinkles, and overall lackluster appearance by neutralizing damaging free radicals. Serums containing vitamin C provide anti-aging benefits because of their potent antioxidant properties. Antioxidant-rich meals provide the fortitude our skin needs to withstand environmental aggressors like ultraviolet radiation, blue light, and more.
- By adding an SPF into your routine
The blue light from screens is just as dangerous as sunlight’s ultraviolet rays. As a result, if you need to spend extended periods in front of a computer screen, you should protect your skin using sunscreen with a high broad-spectrum SPF. Be sure to remember to reapply it to your face.
- By using water-based skin lotion
The heat from a computer can cause dry skin. Therefore it’s important to restore your natural moisture balance. Anoption is to moisturize your face regularly. Your skin will be better hydrated with a water-based moisturizer. Hyaluronic acid-rich skin care products are ideal for moisturizing the skin and reducing the effects of blue light exposure.
- Through frequent facial wash
Washing and cleansing your face after long periods of screen time can eliminate any free radicals that may have formed. Take frequent breaks to prevent eye strain from prolonged computer use. However, use a mild cleanser that won’t strip your skin.
MEDICAL ADVICE DISCLAIMER: All content in this blog and description including: information, opinions, content, references and links is for informational purposes only. The Author does not provide any medical advice on the Site. Accessing, viewing, reading or otherwise using this content does NOT create a physician-patient relationship between you and its’ author. Providing personal or medical information to the Principal author does not create a physician-patient rela-tionship between you and the Principal author or authors. Nothing contained in this blog or it’s description is intended to establish a physician-patient relationship, to replace the services of a trained physician or health care professional, or otherwise to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. You should consult a licensed physician or appropriately-credentialed health care worker in your community in all matters relating to your health.